Published on: April 15, 2022
What is Clostridioides difficile?
Clostridioides difficile, more commonly known as C. diff, is a bacterium-causing infection that affects the large intestine. As a result of this infection, C. diff can cause severe diarrhea and even colitis (inflammation of the colon). If not treated quickly and properly, patients can run the risk of severe infection and hospitalization. Generally, C. diff more commonly affects older patients in hospital settings who are taking antibiotic medications (Mayo Clinic). United States hospitals are now taking preventative measures to ensure the lowest possible number of infections. Annually, there are 200,000 patients infected with C. diff in U.S. hospitals. In addition, outside of hospitals, there are about 170,000 cases annually (Mayo Clinic).
While it is easy to get overwhelmed by the numbers, it is important to understand what the infection is, who is most at-risk, the common symptoms, and how to prevent the spread. By doing so, cases will continue to decrease, and hospitals can maintain a safe and healthy space. Let’s find out more information about C. diff!
Who is Most At-Risk?
Since C. diff is a contagious infection, it is important to remember that anybody can get it. But like any infection, some people are more susceptible to it than others. Understanding who is the most at-risk can help you protect yourself and protect those around you from catching a severe infection. Look at our list below to see if you or someone you know falls in the category of being at-risk for C. diff.
- Over the age of sixty-five.
- People who have recently visited / stayed in a hospital or nursing home.
- Weakened or compromised immune systems, including those taking immunosuppressive drugs.
- Previously had or were exposed to a C. diff infection.
- Currently taking or just finished taking antibiotics (Medications like Clindamycin, Cephalosporins, Penicillin’s, and Fluoroquinolones can increase risk due to the antibiotics destroying helpful bacteria).
Even if you fall under one of these categories, it does not always mean you will get a C. diff infection. Some people may only be carriers of the bacteria, but never get sick. It is important to note that at-risk only means that you are more susceptible to it. Please also note that younger adults can also contract C. diff. For example, Jordan Spieth, a 28-year-old professional golfer, announced in February 2022 that he had Clostridium difficile.
C. diff Causes
C. diff is caused by bacteria being orally ingested and reproducing in the small intestine. After the bacteria has reproduced, it moves towards the large intestine where it releases toxins that cause inflammation and diarrhea. Once this bacterium is outside of the colon, it can survive in a variety of environments:
- Human and animal feces
- Unwashed hands
- Food and Water
- Soil, from decomposed feces
- Surfaces, especially in the bathroom or bedroom
C. diff lives in these environments until ingested to repeat the bacteria’s reproduction cycle inside another person. This is how it is very easily spread in hospitals and nursing homes since patients are close to each other.
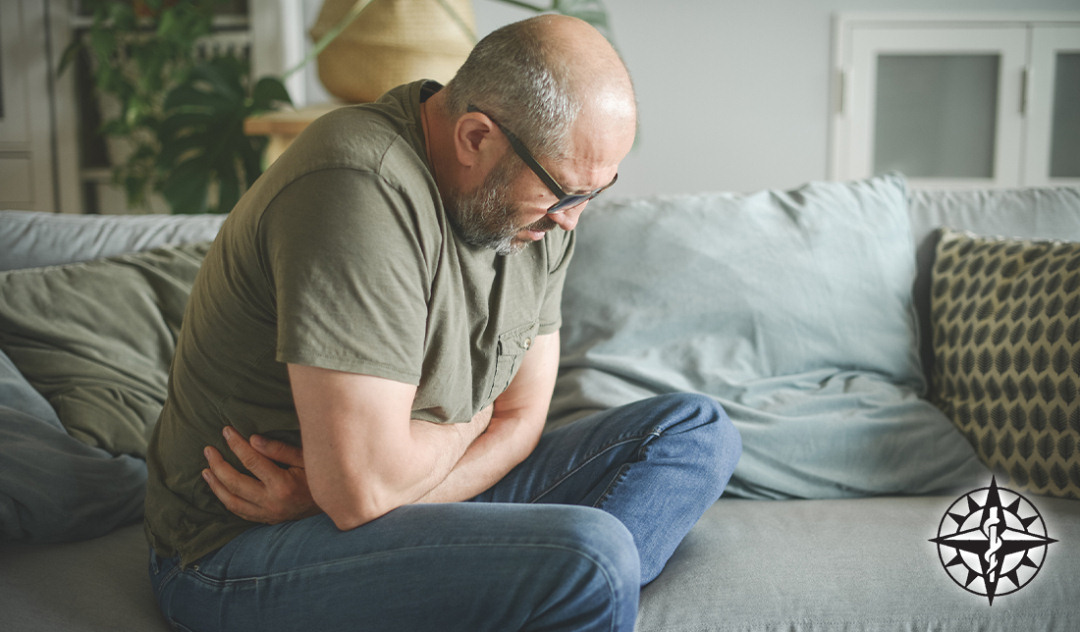
C. diff Symptoms
Within 5 to 10 days of starting antibiotics, you may begin to start experiencing the following symptoms:
- Prolonged watery diarrhea (3+ a day)
- Abdominal cramping or pain
- Fever
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Dehydrated
- Kidney failure
- Weight loss
- Blood or pus in stool
If you have some of these symptoms listed above, we encourage you to get a diagnosis test via stool specimen. Prolonged and untreated symptoms can lead to toxic megacolon and sepsis. These conditions are both extremely serious and can require admission to an intensive care unit. In severe untreated cases, C. diff can lead to death. Overall, C. diff is treatable but can be difficult to get under control if delayed for too long. For some, they may get more severe C. diff symptoms and have a harder time getting rid of the infection. Some people can get it multiple times and even back-to-back.
Learn more about possible symptoms from the Mayo Clinic and the CDC. If you are a visual learner, check out this YouTube video giving a great overview of C. diff below.
C. diff Treatment
Treatments for C. diff can vary depending on the severity of symptoms and how long they have been prolonged. The first approach would be to start an oral antibiotic regime that may last from 10 to 14 days or longer depending on what your doctor decides. In other cases, some patients will receive an additional drug via IV called bezlotoxumab (Up to Date). If a patient has had multiple recurrences of C. diff, a Fecal Microbiota transplant may be recommended. This treatment involves stool from a healthy patient to be administered via a nasogastric tube, colonoscopy, enema, or capsules to an infected patient. This treatment helps regrow the beneficial bacteria and restore the gut microbiome. As a result, C. diff bacteria will be crowded out. Check out this informational video on the gut microbiome and how C. diff impacts it.
Prevent the Spread
While these measures should be taken regardless, here are our top recommendations for preventing the spread of C. diff.
- Wash Your Hands: One of the easiest ways to prevent any bacteria or disease from spreading is by proactively washing your own hands. It is important to note that hand sanitizers and alcohol bases are not enough to kill the spores of C diff. By practicing good hand hygiene, you reduce your chances of getting sick and protect others around you.
- Avoid Prolonged Use of Antibiotics: Although antibiotics are important for killing bad bacteria, they can sometimes kill the healthy bacteria too. Your body needs good bacteria to fight off infection. By limiting your use of antibiotics to only when your doctor recommends, you can keep your good bacteria count up to protect your body!
- Clean, Clean, Clean: Like any other disease that is spread via the fecal-oral route, it is crucial to continuously clean and disinfect surfaces. Bathrooms and bedrooms are both areas that should be cleaned with bleach products to kill any potential C. diff bacteria.
Additional C. diff Resources:
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clostridioides-difficile-infection-in-adults-treatment-and-prevention
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/c-difficile/symptoms-causes/syc-20351691
https://www.cdc.gov/cdiff/what-is.html
https://www.cdc.gov/cdiff/pdf/Cdiff-progression-H.pdf
Let Us Help You | Infectious Disease Associates of Tampa Bay
If you have been diagnosed with C. diff, Infectious Disease Associates of Tampa Bay (IDATB) has physicians who are experienced in treating this condition. In addition, IDATB has access to research studies including those for C diff infection. IDATB provides high-quality healthcare services for patients in the Tampa Bay metro area. If you suspect you may have a C diff infection, IDATB is here to help. With decades of experience, IDATB successfully treats Floridians (or those visiting Tampa who become ill) with infectious diseases while providing an in-house lab for any required testing. If you have any questions or concerns about infectious diseases or C. diff, call IDATB at 813-251-8444.